- PRODUCT DETAIL
- TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Materials for Manufacturing Multilayer Flexible PCBs
The base material, cover film, reinforcing material, and other auxiliary materials are the primary raw materials used in the production of multilayer flexible PCBs.
Substrate
Substrates for multi-layer flexible PCBs are classified as glue-free and non-glue-free.
Adhesive substrate: The adhesive substrate is primarily made up of copper foil, adhesive, and PI. Single-sided adhesive substrates and double-sided adhesive substrates are the two types of adhesive substrates.
Adhesive-free substrate: A substrate that does not have an adhesive layer. Because adhesive-free substrates are thinner, have better dimensional stability, greater heat resistance, greater bending resistance, greater chemical resistance, and so on, they are now widely used.
Cover Film
The cover film is made up of three components: release paper, adhesive, and PI; the only components remaining on the flexible circuit board are adhesive and PI. During the manufacturing process, the release paper will be peeled away.
Reinforcing materials
The reinforcing material is unique to flexible PCBs. Reinforcing material is used in a specific area of the flexible circuit board to increase the supporting strength of that area, thereby compensating for the “flexible” nature of FPC.
Currently, common reinforcement materials include FR4, steel sheet, PI, and aluminum sheet, among others.
Other supplementary materials
Adhesives (pure glue, primarily used for soft and hard bonding boards and bonding FR-4 or steel sheet reinforcement materials to play a bonding role), electromagnetic protective film, and pure Copper foil are other auxiliary materials used for multi-layer flexible PCBs (mainly used in the production of hollow flexible PCB).
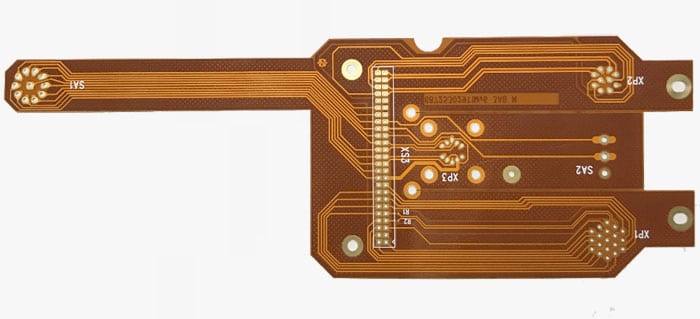
Benefits of Flexible Printed Circuits
Flexible Printed Circuits have numerous advantages, including:
● Assembly Error Reduction: Flex circuits eliminate human errors once associated with hand-built wire harnesses through accurate design and automated production. Circuits are ONLY routed to the points specified in the accurate design plan, with the exception of production-induced errors.
Assembly time and costs are reduced because flex circuits require less manual labor during assembly and reduce production errors. Flex circuits are built with the ability to combine form, fit, and function. Flex circuits eliminate the high costs associated with wire routing, wrapping, and soldering. Instead of individual hard PC boards, complete interconnection systems are installed or replaced. As a result, wiring errors are eliminated, lowering manufacturing costs. Assembly time and costs are reduced whether the production is low volume with a complex circuit or high volume with a simple circuit.
● Flexibility during installation: Because they can interconnect two or more planes during execution, flexible circuits provide a third dimension to work with. As a result, they solve space and weight issues that rigid boards cannot. Without electronic failure, flex circuits can be manipulated many times during installation and execution.
● High Density Applications: Flexible circuits enable minutely narrow lines, allowing for a high density device population. Denser device populations and lighter conductors can be designed into a product, allowing for more product features.
● Improved Airflow: Flex circuits allow for the flow of cooling air through an electronic application due to their streamlined design.
● Increased Heat Dissipation: Because flexible circuits have a higher surface-to-volume ratio and a more compact design, a shorter thermal path is possible. Furthermore, because flex circuits are thinner, heat can be dissipated from both sides of the circuit.
● Increased System Reliability: Most circuit failures in the past occurred at an interconnection point. Flex circuits can be designed to reduce interconnections, which increases a circuit’s reliability.
● Reliability and durability: In designs with moving parts, a flexible circuit can move and flex up to 500 million times without failing. Polyimide’s exceptional thermal stability also allows the circuit to withstand high-temperature applications. Polyimide’s thermal stability makes it a better base for surface mounting than hard boards. A thermal mismatch is less likely to occur because the compliant base film places less stress on soldered joints.
For superior manufacturing consistency, our circuits are made from exact replicas of artwork. The etched circuits completely eliminate wiring errors by replacing the rigid board’s solder and hand wiring connections.
● Simplified Circuit Geometry: Because Flexible Circuit Technologies places surface mount electronics directly onto the circuit, the overall design is simplified. In flex circuits, intricate patterns that were nearly impossible to achieve on rigid boards are easily realized.
● Reduced package size and weight: Multiple systems in rigid boards add weight and take up more space. The dielectric substrates in flex circuits are the thinnest available. Thinness enables a more streamlined design, removing the need for bulky rigid boards. The elasticity and flexibility allow for a reduction in package size. Package weight reduction is an additional benefit, in addition to package size reduction. With the electronics industries’ ever-increasing demands, weight reduction keeps flex circuits competitive.
Advantages Of Multilayer Flexible PCB
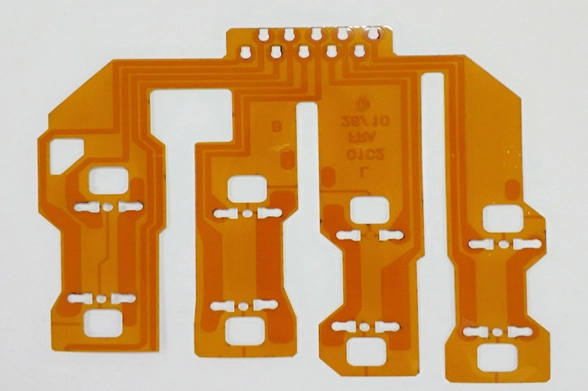
Multilayer flexible PCBs provide several advantages that make them an increasingly popular choice among engineers. Here, we’ll take a closer look at some of the best advantages.
Improved Performance and Dependability
Because of their increased flexibility, multilayer flexible PCBs can withstand more stress and vibration, which can often damage traditional rigid PCBs. Furthermore, multiple layers allow for more efficient signal and power routing, resulting in improved performance and reliability. Multilayer flexible PCBs are frequently chosen for high-end applications requiring extreme performance and reliability.
Weight and Size Reductions
Flexible multi-layer PCBs are lighter and smaller than rigid rigid PCBs. A flexible PCB’s multilayer construction also allows for more efficient use of space, which is important in smaller applications or those with limited space.
Signal Frequency and Bandwidth Have Been Increased
Multilayer flexible PCBs also provide increased signal frequency and bandwidth, which is important in high-speed applications or when dealing with large amounts of data.
Improved Power Efficiency
Improved power efficiency is another advantage of multilayer flexible PCBs. Because multilayer flexible PCBs are more efficient at power routing, they can help improve power efficiency, which is important for applications that require long battery life.
Environmental Compliance Has Improved
A flexible PCB’s multilayer design can also aid in environmental compliance. A multilayer flexible PCB can route signals and power more effectively by using multiple layers, which can help to reduce the amount of radiation and electromagnetic interference emitted by the PCB.
Applications Of Multilayer Flexible PCB
Multilayer flexible PCBs have a wide range of applications. Among the most common are:
Electronic Consumer Goods
Smartphones, e-readers, tablet PCs, and GPS units are just a few examples of consumer electronics products that frequently use multilayer flexible PCBs. High-end printers, desktop computers, laptops, and digital cameras all use multilayer flexible circuits.
Industrial Machinery
Multilayer flexible PCBs are commonly found in industrial equipment. Medical devices, power generation equipment, factory automation hardware, and traffic control equipment are all examples of this.
Components for Automobiles
Flexible multilayer circuits can be found in a wide range of automotive components, from HVsAC to infotainment systems.
Military/Aerospace Equipment
Flexible multilayer circuits are frequently used in the military and aerospace industries. They can be found in a wide range of products, including communication equipment, wearable electronics, and avionics systems.
Additional Applications
Multilayer flexible circuits are also used in the manufacture of industrial machinery, robotics, buoys, and renewable energy devices.
Due to the versatility of multilayer flexible PCBs, manufacturers have begun to offer multilayer flexible PCB assemblies. Because the boards are assembled when they arrive at your facility, you save time and money.

Our Capabilities
We can complete your order for flexible PCB manufacturing in as little as 24 hours. We are ready and eager to make your ideas a reality.
| Specifications | Capabilities |
| Quality Grade | IPC 2 |
| Number of Layers | 1-6 Layers |
| Order Quantity | Not MOQ Requirement |
| Build Time | 1 Day-2 Weeks |
| Material | DuPont PI, Shengyi PI,etc. |
| Board Thickness | 0.1mm-0.8mm |
| Copper Weight (Finished) | 1/3 OZ-3OZ |
| Min Tracing/Spacing | 3Mil/3Mil |
| Solder Mask Color | Green, White, Blue, Black, Red, Yellow |
| Solder-stop coating—Coverlay | PI and PET film |
| Silkscreen Color | White, Black, Yellow |
Why Choose UnitePCB’s Multilayer Flexible PCB Manufacturing Services?
We have a competitive advantage in the PCB industry due to our knowledge and experience in manufacturing flexible printed circuit boards. We also have no minimum order quantity requirements and always promise a competitive price and unbeatable customer service.
Prior to production, our experienced team checks each design and reviews it with you. This ensures that the circuit design is ready for manufacturing and that your boards will perform as expected. Our flex PCB parts and components are guaranteed to be of high quality. If you’d rather talk to us before placing an order, we’re only an email away.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Multilayer Flexible PCB & Multilayer FPCB & Multilayer Flex PCB
| Feature | Parameters |
| 6 Layer flexible PCB& Flex PCB&FPCB | |
| Layer Count | 6-layers |
| Structure | Flex |
| Material | PI FCCL (35μm Cu + 25μm PI + 35μm Cu) |
| FPC Thickness | 0.25mm+/-0.03mm |
| Coverlay | Yellow x2 |
| Silkscreen | White x2 |
| Finished Copper Weight | /35/35μm |
| Surface Finish | Hard Gold Plating (2U) |
| Min NC Drilling Dia | 0.2mm |
| Stiffener | 0.06mm steel stiffener |
| Minimum Trace/space | 0.06MM/0.09MM |
| Application | high speed transmission |